
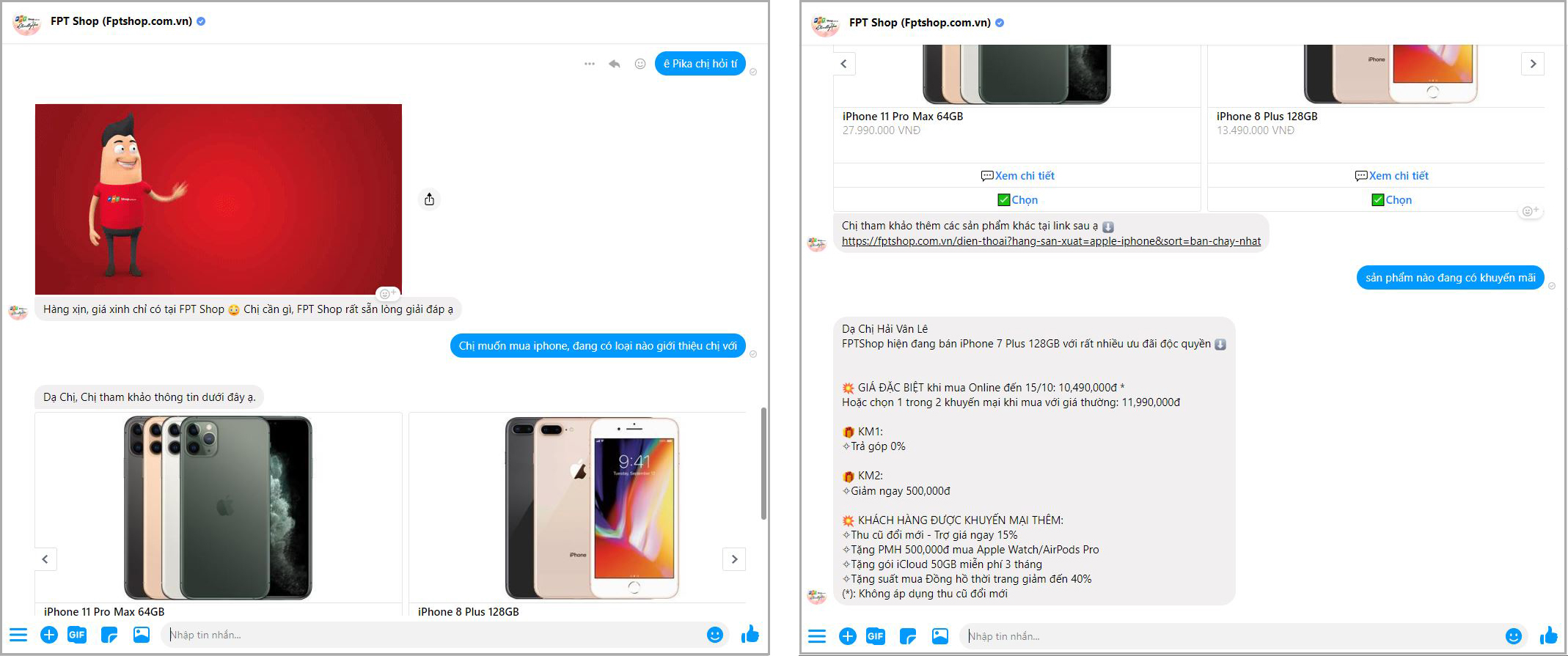
This sort of usage holds the prospect of moving chatbot technology from Weizenbaum's "shelf. Thus, for example, online help systems can usefully employ chatbot techniques to identify the area of help that users require, potentially providing a "friendlier" interface than a more formal search or menu system. Most people prefer to engage with programs that are human-like, and this gives chatbot-style techniques a potentially useful role in interactive systems that need to elicit information from users, as long as that information is relatively straightforward and falls into predictable categories. Interface designers have come to appreciate that humans' readiness to interpret computer output as genuinely conversational-even when it is actually based on rather simple pattern-matching-can be exploited for useful purposes. ELIZA showed that such an illusion is surprisingly easy to generate because human judges are so ready to give the benefit of the doubt when conversational responses are capable of being interpreted as "intelligent". Thus an illusion of understanding is generated, even though the processing involved has been merely superficial. by responding to any input that contains the word 'MOTHER' with 'TELL ME MORE ABOUT YOUR FAMILY'). ĮLIZA's key method of operation (copied by chatbot designers ever since) involves the recognition of clue words or phrases in the input, and the output of the corresponding pre-prepared or pre-programmed responses that can move the conversation forward in an apparently meaningful way (e.g. The object of this paper is to cause just such a re-evaluation of the program about to be "explained". With that thought, he moves the program in question from the shelf marked "intelligent", to that reserved for curios. The observer says to himself "I could have written that". But once a particular program is unmasked, once its inner workings are explained, its magic crumbles away it stands revealed as a mere collection of procedures. In artificial intelligence, machines are made to behave in wondrous ways, often sufficient to dazzle even the most experienced observer. However Weizenbaum himself did not claim that ELIZA was genuinely intelligent, and the introduction to his paper presented it more as a debunking exercise: The notoriety of Turing's proposed test stimulated great interest in Joseph Weizenbaum's program ELIZA, published in 1966, which seemed to be able to fool users into believing that they were conversing with a real human. This criterion depends on the ability of a computer program to impersonate a human in a real-time written conversation with a human judge to the extent that the judge is unable to distinguish reliably-on the basis of the conversational content alone-between the program and a real human. In 1950, Alan Turing's famous article " Computing Machinery and Intelligence" was published, which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence. Recently, companies spanning various industries have begun using the latest generative artificial intelligence technologies to power more advanced developments in such areas. Ī major area where chatbots have long been used is in customer service and support, such as with various sorts of virtual assistants. Chatbots can also be designed or customized to further target even more specific situations and/or particular subject-matter domains. simulating human conversation, in the case of chatbots).
Such examples reflect the recent practice of such products being built based upon broad foundational large language models that get fine-tuned so as to target specific tasks or applications (i.e. Recently this field has gained widespread attention due to the popularity of OpenAI's ChatGPT, followed by alternatives such as Microsoft's Bing Chat (which uses OpenAI's GPT-4) and Google's Bard. Such technologies often utilize aspects of deep learning and natural language processing. Modern chatbots are artificial intelligence (AI) systems that are capable of maintaining a conversation with a user in natural language and simulating the way a human would behave as a conversational partner.
#DENVER AI CHATBOT COMPANIES SOFTWARE#
A virtual assistant chatbot The 1966 ELIZA chatbotĪ chatbot (originally chatterbot ) is a software application that aims to mimic human conversation through text or voice interactions, typically online.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
